- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM
Introduction

Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive worry, fear, or apprehension. These feelings can become overwhelming and interfere with daily life. There are several types of anxiety disorders, each with its own specific symptoms and triggers.
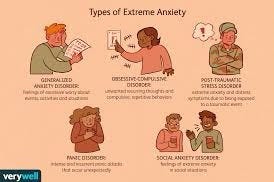
Some common types of anxiety disorders include:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
People with GAD experience persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, even when there’s no apparent reason for concern. This worry can be difficult to control and may lead to physical symptoms such as restlessness, fatigue, muscle tension, and irritability.
- Panic Disorder:
This involves sudden and intense episodes of fear known as panic attacks. These attacks can be accompanied by symptoms such as a racing heart, shortness of breath, chest pain, and a sense of impending doom.
- Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia):
Individuals with social anxiety disorder have an intense fear of social situations and interactions. They may be excessively self-conscious and worry about being judged or embarrassed in public.
- Specific Phobias:
Specific phobias involve an intense fear of a particular object, situation, or activity. Common examples include fear of heights, flying, spiders, or enclosed spaces.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
OCD involves intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) aimed at reducing the distress caused by these thoughts. Common obsessions include fears of contamination or harming others, while compulsions often involve repeated rituals or behaviors.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
PTSD can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, and heightened emotional responses, often leading to avoidance of reminders of the traumatic event.
- Separation Anxiety Disorder:
This is characterized by excessive worry and fear related to being separated from loved ones or attachment figures. It’s more commonly diagnosed in children but can also affect adults.
Anxiety disorders can have a significant impact on a person’s life, affecting relationships, work, and overall well-being. Effective treatments are available and often involve a combination of psychotherapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy), medication (like antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs), and lifestyle changes.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of an anxiety disorder, seeking professional help from a mental health provider is important. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can lead to better management of symptoms and an improved quality of life. It should be noted that, QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
RISK FACTORS AND CAUSES
The exact causes of anxiety disorders are not fully understood, but they are thought to result from a complex interplay of biological, genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Some key contributors include:
- Genetics:
There is evidence that genetics play a role in the development of anxiety disorders. If a close family member has an anxiety disorder, you may be at a higher risk of developing one yourself.
- Brain Chemistry:
Imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain, are associated with anxiety disorders. For instance, an imbalance in serotonin, which regulates mood, can contribute to anxiety.
- Environmental Factors:
Traumatic or stressful life events, such as childhood trauma, abuse, or major life changes, can increase the risk of developing an anxiety disorder. Chronic stress and exposure to ongoing stressful situations can also contribute.
- Brain Structure:
Brain regions responsible for regulating emotions and processing fear responses, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, may function differently in individuals with anxiety disorders.
- Personality Traits:
Certain personality traits, such as being overly cautious, perfectionistic, or having a tendency to worry excessively, can increase vulnerability to anxiety disorders.
- Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as heart disease, thyroid disorders, and chronic pain, can be associated with increased anxiety.
- Substance Abuse:
The use of drugs or alcohol can exacerbate or trigger anxiety symptoms. Additionally, withdrawal from substances can also lead to anxiety.
- Neurodevelopmental Factors:
Anxiety disorders can sometimes emerge during childhood or adolescence, suggesting that neurodevelopmental factors may contribute.
- Learned Behavior:
Observing and imitating anxious behaviors from family members or significant others can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders.
It’s important to note that anxiety disorders are not caused by a single factor but rather arise from a combination of factors. Additionally, different individuals may experience anxiety disorders due to varying combinations of these factors. While it may not be possible to pinpoint a single cause, understanding these contributing factors can guide treatment approaches and interventions for managing anxiety disorders effectively.
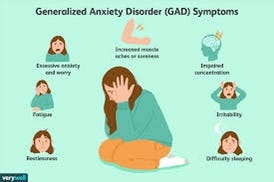
SPOTTING THE SIGNS OF ANXIETY
Anxiety disorder symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific type of anxiety disorder and the individual’s experiences. However, there are common symptoms that people with anxiety disorders may experience. These symptoms can be both emotional and physical. Here are some general symptoms associated with anxiety disorders:
- Excessive Worry:
Persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, even when there’s no clear reason for concern.
- Restlessness:
Feeling on edge, unable to relax, and often experiencing a sense of restlessness or irritability.
- Difficulty Concentrating:
Finding it hard to concentrate or focus on tasks due to intrusive anxious thoughts.
- Muscle Tension:
Physical tension, muscle aches, and soreness, often related to the body’s response to stress and anxiety.
- Sleep Disturbances:
Trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restless, unsatisfying sleep due to racing thoughts and anxiety.
- Panic Attacks:
Intense episodes of fear or panic characterized by symptoms like a racing heart, sweating, trembling, shortness of breath, chest pain, and a feeling of impending doom.
- Avoidance Behavior:
Going to great lengths to avoid situations or places that trigger anxiety or panic.
- Physical Symptoms:
Experiencing a range of physical symptoms like dizziness, nausea, sweating, tingling sensations, and difficulty breathing.
- Excessive Self-Consciousness:
Feeling overly self-conscious and fearful of being judged by others, often leading to avoidance of social situations.
- Obsessive Thoughts and Compulsions:
Recurring intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and engaging in repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) to alleviate anxiety.
- Fear of Losing Control:
A persistent fear of losing control, going crazy, or doing something embarrassing in public.
- Physical Symptoms of Anxiety:
Rapid heartbeat, shallow breathing, dry mouth, upset stomach, and trembling.
- Hypervigilance:
Being overly alert and on the lookout for potential threats, even in situations where no real danger exists.
- Difficulty Relaxing:
Finding it challenging to relax and experience a sense of calm due to ongoing anxiety.
It’s important to note that anxiety disorders can affect people differently, and individuals may experience a combination of these symptoms to varying degrees. If these symptoms persist and significantly interfere with daily functioning, seeking professional help from a mental health provider is recommended. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can lead to effective management of anxiety disorders and an improved quality of life.
Treatment and Medications

The treatment of anxiety disorders often involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. The specific approach can vary based on the type of anxiety disorder, the severity of symptoms, and the individual’s preferences. Here are some common treatment options:
- Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy):
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
This is a widely used approach that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. CBT helps individuals develop coping strategies and practical skills to manage anxiety.
-
Exposure Therapy: This is particularly effective for specific phobias and PTSD. It involves gradually exposing the person to the feared object or situation in a controlled manner to reduce the anxiety response.
-
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): This approach helps individuals accept their anxious thoughts and feelings while taking actions aligned with their values and goals.
-
.Mindfulness-Based Therapies: Techniques like mindfulness meditation can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and feelings without judgment, which can reduce anxiety.
-
Medication:
. Antidepressants:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are commonly prescribed to treat anxiety disorders. They help regulate neurotransmitters and can provide relief from symptoms.
. Benzodiazepines:
These are sedative medications that can provide short-term relief from severe anxiety. However, they are usually prescribed cautiously due to the risk of dependence and potential side effects.
- Lifestyle Changes
. – Regular Exercise:Physical activity can help reduce anxiety by promoting the release of endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers.
. – Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in nutrients can contribute to overall well-being and support brain health.
. – Adequate Sleep: Prioritize good sleep hygiene to improve mood and reduce anxiety.
. – Stress Management: Learning relaxation techniques, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help manage stress and anxiety.
-
Support Groups: Participating in support groups or therapy groups with others who experience similar challenges can provide a sense of understanding and community.
-
Self-Care: Engaging in activities that bring joy, practicing self-compassion, and finding healthy outlets for stress can contribute to anxiety management.
It’s important to work closely with a qualified mental health professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific situation. Treatment is often individualized, and what works for one person may not work for another. Regular communication with your healthcare provider is key to monitoring progress and making any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. If you or someone you know is experiencing severe anxiety symptoms, it’s important to seek help promptly to improve overall well-being and quality of life. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
Preventative measures
While it may not be possible to completely prevent anxiety disorders, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of developing them or to manage anxiety more effectively:
- Healthy Lifestyle:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact your mental well-being. Engage in regular exercise, eat a balanced diet, and prioritize sufficient sleep.
- Stress Management:
Develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress, such as relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, and yoga.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine:
Excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Moderation is key.
- Avoid Drug Abuse:
Substance abuse can contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety disorders. Avoid using illicit drugs and misuse of prescription medications.
- Seek Support:
Reach out to friends, family members, or support groups when you’re feeling overwhelmed. Social support can provide a buffer against anxiety.
- Address Childhood Trauma:
If you’ve experienced childhood trauma or adverse experiences, seeking therapy to address and process these experiences can reduce the risk of anxiety disorders.
- Manage Expectations:
Set realistic expectations for yourself and your life circumstances. Avoid striving for perfection and accept that setbacks are a natural part of life.
- Develop Strong Coping Skills:
Enhance your problem-solving and resilience skills to better handle life’s challenges.
- Practice Self-Care:
Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation. Make self-care a regular part of your routine.
- Regular Check-ins:
Regularly evaluate your mental and emotional well-being. If you notice persistent anxiety symptoms, seek professional help early.
- Mindfulness and Meditation:
Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help you become more aware of your thoughts and emotions, allowing you to manage them more effectively.
- Professional Help:
If you have a family history of anxiety disorders or are experiencing significant anxiety symptoms, consider seeking professional help from a mental health provider. Early intervention can make a difference in managing or preventing the onset of anxiety disorders.
Remember that it’s normal to experience some level of anxiety from time to time, but when anxiety becomes chronic, overwhelming, or interferes with daily life, seeking help is crucial. Mental health professionals can provide guidance, support, and evidence-based strategies to manage anxiety and improve overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Of course! Here are some frequently asked questions about anxiety disorders:
- What is a panic attack?
. – A panic attack is a sudden episode of intense fear or discomfort, accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, and a feeling of impending doom.
- Can children and teenagers have anxiety disorders?
. – Yes, anxiety disorders can affect people of all ages, including children and adolescents. It’s important to recognize and address anxiety in young individuals.
- Can anxiety disorders be cured?
. – While anxiety disorders may not always be fully cured, effective treatment can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Many people learn to manage their anxiety successfully.
- Is it possible to have more than one anxiety disorder?
. – Yes, it’s common for individuals to experience more than one anxiety disorder simultaneously or at different points in their lives.
Remember that every individual’s experience with anxiety disorders can be unique. If you have specific questions or concerns about anxiety disorders, it’s best to consult with a mental health professional who can provide personalized guidance and information based on your situation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anxiety disorders are complex mental health conditions that can affect anyone, regardless of age or background. They manifest as excessive worry, fear, and apprehension that can disrupt daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for individuals dealing with anxiety and those seeking to support them. Psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments are effective tools for managing anxiety disorders.
It’s important to recognize that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety symptoms, reaching out to a mental health professional can lead to proper diagnosis, personalized treatment, and improved well-being. While complete prevention may not always be possible, adopting a healthy lifestyle, stress management techniques, and a supportive network can contribute to anxiety prevention and effective coping strategies.
By fostering understanding, raising awareness, and promoting open conversations about mental health, we can collectively work toward reducing the stigma surrounding anxiety disorders and creating a more compassionate and informed society. Remember, you’re not alone, and help is available.
To know more about QMe , click ,
QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer