- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
Definition and overview
A bacterial infection called streptococcal pharyngitis, which affects the tonsils and throat, is brought on by Streptococcus pyogenes. Common in children and adolescents, it spreads through respiratory droplets or contact with infected surfaces. Severe painful throat, fever, and swollen tonsils are symptoms. Swabs taken from the throat can detect infections early, which enables quick antibiotic treatment and lowers the risk of sequelae like rheumatic fever. Practicing good hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals aid in prevention. Strep throat is treatable with antibiotics, ensuring a speedy recovery when the full course is completed.
Prevalence and common age groups affected
Strep throat is prevalent worldwide, with millions of cases reported annually. Children and teenagers between the ages of 5 and 15 are the ones that are most frequently affected. But it can also affect adults of any age, particularly those who are in close proximity to infected people or are in crowded places like daycare centers and schools.
Causes and Transmission

bacteria belonging to the group A streptococcus
A form of bacteria called Group A Streptococcus (GAS), commonly referred to as Streptococcus pyogenes, is to blame for a number of illnesses that affect people. It is one of the most prevalent organisms connected to strep throat (streptococcal pharyngitis), as well as other conditions like impetigo, cellulitis, and skin infections. GAS can spread through respiratory droplets or direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces. To stop the spread of the bacteria and associated side effects from GAS infections, prompt identification and adequate antibiotic treatment are crucial.
Modes of transmission
When an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or talks, respiratory droplets of Group A Streptococcus (GAS) are released into the air. It can also transmit through direct contact with infected saliva or nasal secretions, and by touching contaminated surfaces. Good hygiene practices, such as covering the mouth while coughing and frequent handwashing, can help prevent transmission.
Signs and Symptoms
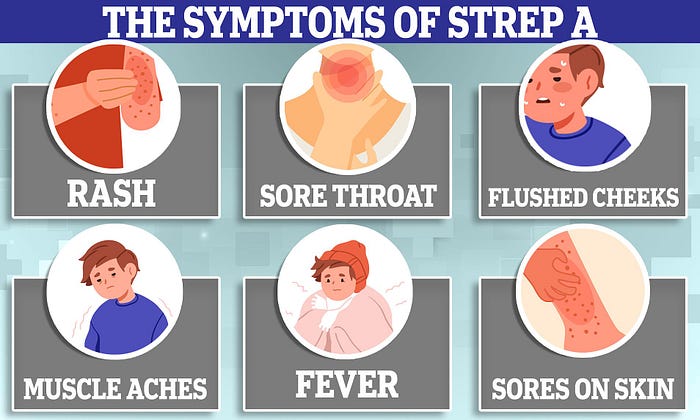
A. A sour throat and difficulty swallowing: A sore throat and trouble swallowing are symptoms of strep throat, which is brought on by inflammation and infection of the tonsils and throat lining by the streptococcus bacterium.
B. Tonsils that are red and swollen: The inflammatory response to the Streptococcus bacterium that causes strep throat frequently results in tonsils that are red and swollen. The tonsils may look swollen and their surface may have white or yellow spots or patches.
C. Fever and chills: These symptoms typically accompany strep throat when the body’s immune system responds to the bacterial infection. Even though the body frequently experiences chills when attempting to regulate its temperature, the rise in body temperature helps the body fight the illness.
D. Body aches: Body aches and headaches are typical signs of strep throat. Inflammation brought on by the bacterial infection results in the release of certain chemicals, which can induce headache and broad bodily discomfort.
E_. Rash (scarlet fever), occasionally_: Strep throat can occasionally progress to scarlet fever, which is distinguished by a characteristic rash. The rash often begins on the chest and belly before spreading to other locations. It looks like little red dots and gives the skin a rough texture.
Diagnosis
A combination of clinical examination and laboratory tests are used to diagnose strep throat. The medical professional looks for typical signs such a sore throat, red and swollen tonsils, and swollen lymph nodes during a physical examination. They may also look for the presence of a scarlet fever rash.
In order to obtain a sample from the back of the throat, a throat swab is frequently used. This sample is then tested using a rapid strep test, which provides quick results within minutes. Even though a throat culture takes longer to complete (about 24–48 hours), it is sometimes used to confirm the diagnosis.
It is crucial to diagnose strep throat accurately to differentiate it from other throat infections and viral illnesses that may have similar symptoms. Early identification guarantees the administration of the proper medications to treat symptoms, shorten the course of the illness, and avoid problems related to streptococcal infections.
Complications
Strep throat, if left untreated or inadequately treated, can lead to several potential complications. The most serious complications include:
-
Rheumatic fever: An inflammatory condition that can damage the heart valves and other tissues, leading to long-term heart problems.
-
A kidney disease that produces inflammation and impairs the kidneys’ capacity to remove waste from the blood is post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Peritonsillar abscess, otitis media (ear infection), sinusitis, and other less frequent side effects are also possible.
To prevent complications, early diagnosis and proper treatment with antibiotics are essential. To guarantee the elimination of the bacteria and lower the risk of problems, it is essential to finish the entire course of antibiotics as directed by the healthcare professional. Seeking medical attention for persistent or worsening symptoms is important to address any potential complications promptly.
Treatment

Antibiotics are typically used to treat strep throat in order to get rid of the Streptococcus bacteria and reduce symptoms. Antibiotics including penicillin, amoxicillin, and cephalosporins are frequently administered. To ensure complete eradication of the germs and lower the risk of problems, patients are encouraged to finish the entire course of antibiotics.
In addition to antibiotics, over-the-counter painkillers such acetaminophen or ibuprofen for fever, sore throat, and body pains can be used to relieve symptoms. Throat lozenges or warm saltwater gargles may also help soothe the throat.
Regarding the role of QMe Healthcare Software System, it can streamline the diagnosis and treatment process for strep throat. QMe software may provide clinical decision support tools to aid healthcare providers in accurately diagnosing strep throat, interpreting test results, and determining appropriate antibiotic treatment. Additionally, the software system can help manage patient data, treatment plans, and follow-up care efficiently, improving overall patient outcomes and healthcare provider workflow.
A. Penicillin and amoxicillin are popular antibiotics recommended to treat strep throat. Other antibiotics include amoxicillin and erythromycin.
They target and eliminate the Group A Streptococcus bacterium responsible for the infection, helping to relieve symptoms and prevent complications when taken as prescribed.
B. Symptomatic relief (painkillers, throat lozenges, etc.): To treat the symptoms of strep throat, you can use over-the-counter painkillers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to lower your temperature, soothe your sore throat, and ease body pains. Throat lozenges and warm saltwater gargles can help soothe the throat and provide temporary relief from discomfort.
Prevention

Preventing strep throat involves several measures. Transmission can be reduced by following good hygiene habits such routine hand washing, covering the mouth and nose while coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with infected people. Cleaning up after yourself on a regular basis and sanitizing frequently touched surfaces can help lessen the chance of contamination. Furthermore, receiving a vaccination against specific streptococcal diseases may add to your protection. People can be informed about the value of early diagnosis and healthcare treatment, which can result in fast management and stop the bacteria’s spread. The prevalence of strep throat and its possible consequences can be considerably decreased by a combination of preventive actions.
Prognosis and Recovery
With prompt and effective healthcare treatment, the prognosis for strep throat is typically very good. After beginning antibiotics, the majority of patients begin to feel better within a few days, and the infection is typically completely gone within a week. However, complications including rheumatic fever and kidney problems could develop in the absence of appropriate therapy. Completing the full course of antibiotics is crucial to prevent relapse and further spread of the bacteria. People can totally recover and go back to their regular activities with rest, water, and obedience to medical recommendations. Seeking medical attention for persistent or worsening symptoms is essential for a smooth recovery and to prevent potential complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Group A Streptococcus, which causes strep throat, is a common and curable bacterial infection of the tonsils and throat. Timely diagnosis through tools like Qme Healthcare Software System can lead to appropriate treatment with antibiotics, providing effective symptom relief and preventing complications. Additionally, symptomatic relief with pain relievers and throat lozenges aids in easing discomfort during recovery. The prevalence of strep throat can be significantly decreased by taking preventive steps, such as maintaining excellent hygiene and getting vaccinated. Overall, early detection, proper treatment, and adherence to medical advice contribute to a positive prognosis and successful recovery, ensuring individuals can swiftly resume their daily activities with minimal disruption.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer