- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
WHAT DO YOU MEAN BY INFERTILITY?

Infertility is a medical condition characterised by the inability of a person or a couple to conceive a child after a year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. It can affect both men and women and may have various causes, including hormonal imbalances, structural problems, reproductive disorders, or other underlying health issues.
DELVING INTO THE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY
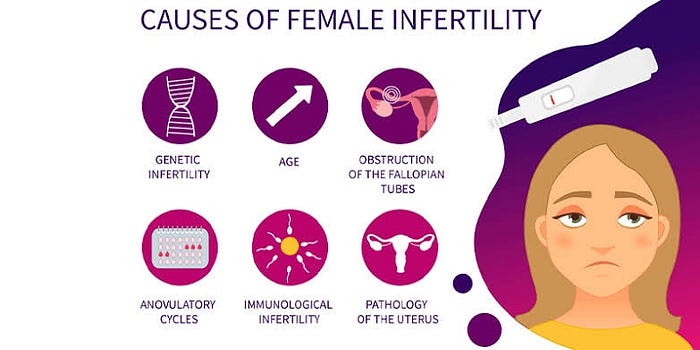
It’s important to note that infertility can be a complex issue, and it may involve a combination of factors. Let’s delve into more detail about the potential causes of infertility in both men and women:
Causes of Infertility in Women:
1.Ovulation Disorders:Problems with ovulation can be caused by hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome ( PCOS), hypothalamic dysfunction, or premature ovarian failure.
-
Fallopian Tube Blockage or Damage: Conditions like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or previous pelvic surgeries can lead to scarring or blockage of the fallopian tubes, hindering the egg’s journey to meet the sperm.
-
Uterine Conditions: Structural abnormalities in the uterus, such as uterine fibroids, polyps, or congenital malformations, can affect implantation or increase the risk of miscarriage.
-
Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, potentially affecting the function of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic structures.
-
Age: Female fertility naturally declines with age, especially after the age of 35, due to a decrease in the quantity and quality of eggs.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal disorders, such as thyroid dysfunction or high levels of prolactin, can interfere with ovulation and fertility.
-
Cervical Issues: Abnormalities in the cervix, such as the production of hostile cervical mucus, can impede the sperm’s ability to reach the egg.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Certain autoimmune conditions can affect the reproductive system and cause infertility.
Causes of Infertility in Men:
1.Low Sperm Count (Oligospermia): Reduced sperm production or abnormal sperm shape (morphology) can lower the chances of fertilization.
-
Poor Sperm Motility (Asthenospermia): Sperm with limited mobility may struggle to reach and penetrate the egg.
-
Structural Abnormalities: Issues with the testicles, epididymis, or vas deferens can affect sperm production and delivery.
-
Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum can raise testicular temperature, potentially impairing sperm production.
-
Ejaculation Disorders: Conditions like retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis, can affect fertility.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal issues, such as low testosterone or elevated levels of prolactin, can impact sperm production and function.
-
Genetic Factors: Inherited genetic conditions can cause infertility or increase the risk of passing on genetic disorders.
-
Infections: Some infections, such as sexually transmitted infections, can affect sperm production or cause scarring in the reproductive tract.
-
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors: Exposure to toxins, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, drug use, and certain medications can adversely affect male fertility.
-
Retrograde Ejaculation: A condition where semen enters the bladder instead of being expelled through the penis during ejaculation, resulting in reduced sperm available for fertilisation.
QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionise healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimised appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalised care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes. If you or your partner suspect infertility, consulting with a healthcare professional or a fertility specialist is crucial to identify the specific cause and explore potential treatment options. They can conduct comprehensive evaluations and provide personalised guidance based on your unique situation.
SPOTTING THE SIGNS: SYMPTOMS OF INFERTILITY
Here is a detailed explanation of the symptoms of infertility a person may experience-
Symptoms in Women:
-
Irregular or Absent Menstrual Periods: Women with irregular menstrual cycles may have difficulty predicting when they are ovulating, which can make it challenging to conceive. Absent periods (amenorrhea) can also indicate a potential problem with ovulation or hormonal imbalances.
-
Painful Periods:
Severe menstrual cramps and pelvic pain (dysmenorrhea) may be associated with conditions like endometriosis or uterine fibroids, which can affect fertility.
- Abnormal Bleeding:
Unusual or heavy bleeding between periods or after intercourse may be a sign of an underlying condition that can impact fertility.
-
Pain During Intercourse: Painful intercourse (dyspareunia) can be related to infections, endometriosis, or other issues affecting the reproductive organs.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Excessive facial hair growth, acne, or other signs of hormonal disturbances may suggest potential fertility-related concerns.
-
Changes in Libido: A decrease in sexual desire or changes in libido may affect the frequency of intercourse, impacting the chances of conception.
Symptoms in Men:
-
Changes in Sexual Function: Difficulties with maintaining an erection, ejaculating, or decreased sexual desire might indicate potential male infertility issues.
-
Pain or Swelling in the Testicles:Discomfort or swelling in the testicles could be related to infections, varicoceles (enlarged veins), or other conditions that may affect sperm production.
-
Abnormal Breast Growth (Gynecomastia): Gynecomastia, the development of breast tissue in men, could be linked to hormonal imbalances that may impact fertility.
-
Changes in Facial or Body Hair Growth:Changes in hair growth patterns might suggest hormonal issues that can contribute to male infertility.
It’s important to note that these symptoms alone do not confirm infertility, as they can be caused by various factors unrelated to fertility. Infertility is diagnosed through comprehensive medical evaluations, including physical examinations, medical histories, and fertility tests for both partners. If you are concerned about your fertility or experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s best to seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional or a fertility specialist for a proper assessment and personalised advice.Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
TREATMENT AND MEDICATIONS
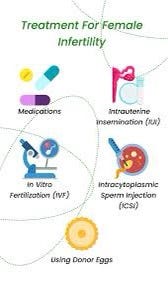
The treatment for infertility varies depending on the underlying cause and individual circumstances. Here are some common treatment options that fertility specialists may consider:
-
Ovulation Induction: For women with ovulation disorders, medications such as Clomiphene or Letrozole can help stimulate egg release.
-
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI):
This involves placing sperm directly into the uterus during ovulation to increase the chances of fertilisation.
- In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF):
IVF involves retrieving eggs, fertilising them with sperm in a laboratory, and transferring the resulting embryos back into the uterus.
-
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): Used in conjunction with IVF, ICSI involves directly injecting a single sperm into an egg to aid fertilisation in cases of male infertility.
-
Surgery:
Surgical procedures may be recommended to correct anatomical issues, remove fibroids or cysts, repair blocked fallopian tubes, or address other structural problems affecting fertility.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
These include various advanced fertility treatments like egg freezing, embryo freezing, and using donor eggs or sperm.
- Hormone Therapy:
Hormonal imbalances in both men and women can be treated with hormone therapies to improve fertility.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
Adopting a healthier lifestyle, managing stress, and avoiding substances harmful to fertility (like smoking and excessive alcohol) can positively impact fertility.
- Genetic Testing and Counseling:
Genetic testing may be recommended to identify potential risks of passing on genetic disorders. Genetic counselling can help individuals make informed decisions.
It’s essential to note that the choice of treatment will depend on factors such as age, overall health, the cause of infertility, and the preferences of the individuals or couples involved. Not all treatments may be suitable or necessary for everyone. Fertility specialists work closely with patients to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to their unique needs and circumstances.
If you are facing infertility concerns, it’s best to consult with a qualified fertility specialist who can conduct a thorough evaluation and recommend the most suitable treatment options for you. They can provide guidance, support, and expertise throughout the journey to help improve the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
PREVENTATIVE MEASURES
While infertility can sometimes be caused by factors beyond one’s control, there are steps individuals and couples can take to potentially reduce the risk of fertility issues. Here are some preventive measures that may help:
-
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can positively influence fertility for both men and women.
-
Avoid Smoking, Alcohol, and Drugs: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use have been linked to decreased fertility in both men and women. Avoiding or minimizing these substances can be beneficial.
-
Manage Stress: High levels of stress can affect hormone levels and disrupt the reproductive system. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and seeking support can be helpful.
-
Protect Against Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Some STIs can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to infertility in women. Practicing safe sex and getting regular STI screenings can help prevent this.
-
Be Cautious with Medications: Certain medications can affect fertility, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any new medications, especially if trying to conceive.
-
Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Minimize exposure to toxins in the environment, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals, which could potentially impact fertility.
-
Monitor and Track Ovulation: For women trying to conceive, understanding their menstrual cycle and tracking ovulation can optimize the timing of intercourse.
-
Seek Early Medical Evaluation: If you’ve been trying to conceive without success for a year (or six months if you’re over 35), it’s advisable to seek an evaluation by a fertility specialist to identify any potential issues early on.
-
Consider Genetic Testing: If there is a family history of genetic disorders, consider genetic testing to assess potential risks and make informed decisions.
It’s important to remember that while these preventive measures can support reproductive health, they do not guarantee fertility. If you have concerns about fertility or are experiencing difficulties in conceiving, consult with a healthcare provider or a fertility specialist. They can provide personalized advice, perform necessary tests, and offer appropriate treatments or interventions tailored to your specific situation.Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
When to see a doctor?
You probably don’t need to see your health care provider about infertility unless you have been trying regularly to get pregnant for at least one year. Women should talk with a care provider earlier, however, if they:
- Are age 35 or older and have been trying to conceive for six months or longer
- Are over age 40
- Have irregular or absent periods
- Have very painful periods
- Have known fertility problems
- Have been diagnosed with endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease
- Have had multiple miscarriages
- Have undergone treatment for cancer
Men should talk to a health care provider if they have:
- A low sperm count or other problems with sperm
- A history of testicular, prostate or sexual problems
- Undergone treatment for cancer
- Small testicles or swelling in the scrotum
- Others in your family with infertility problems
Risk factors
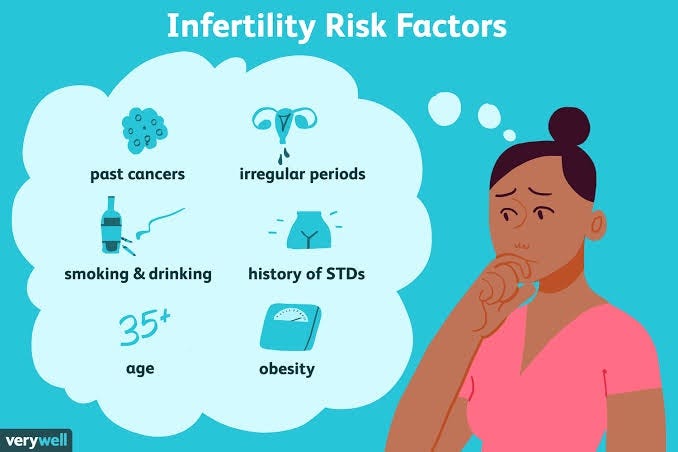
Many of the risk factors for both male and female infertility are the same. They include:
Age-
Women’s fertility gradually declines with age, especially in the mid-30s, and it drops rapidly after age 37. Infertility in older women is likely due to the lower number and quality of eggs, and can also be due to health problems that affect fertility. Men over age 40 may be less fertile than younger men.
Tobacco use-
Smoking tobacco or marijuana by either partner may reduce the likelihood of pregnancy. Smoking also reduces the possible effectiveness of fertility treatment. Miscarriages are more frequent in women who smoke. Smoking can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction and a low sperm count in men.
Alcohol use-
For women, there’s no safe level of alcohol use during conception or pregnancy. Alcohol use may contribute to infertility. For men, heavy alcohol use can decrease sperm count and motility.
Being overweight-
Among American women, an inactive lifestyle and being overweight may increase the risk of infertility. For men, sperm count also may be affected by being overweight.
Being underweight-
Women at risk of fertility problems include those with eating disorders, such as anorexia or bulimia, and those who follow a very low-calorie or restrictive diet.
Exercise issues-
A lack of exercise contributes to obesity, which increases the risk of infertility. Less often, ovulation problems may be associated with frequent strenuous, intense exercise in women who are not overweight.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, infertility is a medical condition characterised by the inability to conceive after a year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. It can affect both men and women and may have various causes, including hormonal imbalances, structural issues, reproductive disorders, or underlying health conditions. While infertility can be a challenging and emotionally distressing experience, there are various treatment options available, such as ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination (IUI), in vitro fertilization (IVF), and surgical interventions.
Preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, managing stress, and seeking early medical evaluation, can also play a significant role in promoting reproductive health. If you or someone you know is facing infertility concerns, it’s essential to seek support from a qualified healthcare provider or a fertility specialist. They can provide personalized guidance, conduct necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatments to help increase the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
Remember that every situation is unique, and infertility treatments and outcomes can vary from person to person. With the right support and care, many individuals and couples can find solutions and embark on their journey towards parenthood.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer